What is basal temperature?
This term, in preparation for and during pregnancy, is firmly part of every woman's vocabulary, so it seems that it is somehow connected with reproductive health. In fact, the word “basal” only means “basic, basic” and emphasizes the following fact: during the day, the body temperature of any person can vary significantly. After a gym session or a hearty lunch, it will be higher than while watching the news while lying on the couch. Temperature measured during the day carries little information about a person’s condition; only the lowest temperature point during the day matters, and it is this that is called basal.
Basal temperature is measured at the moment of greatest relaxation - in the first minutes after waking up, and a graph of its changes over several days can tell a lot. Particularly during the menstrual cycle, it can help calculate the day of ovulation.
Measuring body temperature in children
Pediatrician of the highest category, room No. 6 Olga Ivanovna Tkachenko
A constant body temperature is maintained and regulated by the center of the diencephalon, which continuously records the temperature of the blood flowing through the vessels of the brain.
In children, metabolic processes are more intense, and the mechanisms of thermoregulation are not yet perfect, so their temperature is higher than in adults and can be 370-37.20 C.
In a healthy child, physiological temperature fluctuations are possible during the day, depending on certain conditions (food, excess clothing, ambient temperature, time of year, etc.).
The maximum body temperature is recorded in the afternoon (between 5 and 9 p.m.), and the minimum in the early morning (3 and 6 a.m.).
In summer, body temperature is usually 0.10-0.50 C higher than in winter.
Many infectious and non-infectious diseases cause a restructuring of thermoregulation processes, and the leading symptom is an increase in temperature. It can rise from 36.60-390 C and above and remain at this level for several days.
Measuring temperature is called thermometry. The “manual” approach to measuring body temperature will not provide confidence and will not replace the readings of a thermometer.
How to measure temperature correctly:
Body temperature is measured in the armpit, rectum, oral cavity no earlier than 30 minutes after eating, and in the groin fold.
Electronic, infrared thermometers have appeared, the use of which does not require contact with the child’s skin. Each thermometer has its own advantages and disadvantages.
More accurate: mercury and galinstan (without mercury) thermometers. Which thermometer to use is the mother’s choice.
-Before measuring the temperature, first wipe the armpit dry (the data may be underestimated), press the shoulder tightly to the chest.
-Measurement duration is 7-10 minutes.
-Normal values: 36.20-36.90C.
-Children no older than 5 months. Place the thermometer rectally (in the butt).
Rectal thermometers differ from regular thermometers by having a shorter and rounded end containing mercury. It is inserted with the end lubricated with Vaseline 2.5 cm into the anus carefully without using force, the measurement duration is 1-2 minutes. Rectal temperature is usually 1 degree higher than oral temperature. Normal: 36.80-37.60C.
-In cases where the temperature is measured in the oral cavity, the thermometer is placed under the tongue not directly, but in one of the “pockets” located in the mouth on both sides. These "pockets" are closer to the blood vessels, which reflect the body's core temperature. The norm is 36.60-37.20C. Hold the thermometer for 3 minutes with your lips, not your teeth, breathe through your nose, then the room temperature will not affect the readings. In children under 6 years of age, a temperature measured in the mouth of 380 C may cause seizures.
-When measuring body temperature in the groin area, the child’s leg is bent at the hip joint.
-Thermometry is usually carried out 2 times a day. In the morning (from 6 to 8 o'clock) and in the evening (from 17 to 19 o'clock). In some cases, for example, with fever, there is a need for more frequent measurements (every 2-3 hours).
-After measuring the temperature, mercury and galinstan thermometers are wiped with a disinfectant solution or washed in cool soapy water.
-Electronic thermometers are equipped with instructions, follow them, change the battery every 2 years.
-Store thermometers in special packaging and out of the reach of children.
List of references used in preparing the article:
1. Basics of general nursing /A. L.Grebnev., A.A.Sheptulin. - Moscow: Medicine, 1991.
2. Fundamentals of hygiene and sanitation / D.V. Kolesov, R.D. Mash. — Moscow: Enlightenment, 2009
What basal temperature should be during ovulation?
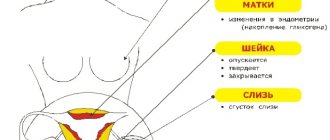
A woman’s body temperature during reproductive age changes under the influence of hormones, and it is not always equal to the classic 36.6 °C. The basal temperature already in the early stages of pregnancy rises to a more comfortable temperature for the fetus - slightly above 37 °C. However, it is much more important to understand how it behaves during the menstrual cycle: along with the concentration of luteinizing hormone in the blood and urine, a change in this indicator is one of the main signs of ovulation.
With the onset of menstruation, the basal temperature rises slightly, then drops to normal and remains at this level throughout the first phase of the menstrual cycle. Just before ovulation, due to rising estrogen levels, it briefly dips below normal. From the moment of ovulation, the production of estrogen decreases and progesterone increases, so the temperature rises sharply above the initial level and stays there throughout the second phase of the cycle, slowly decreasing every day.
The changes described above at the beginning of a possible pregnancy are, in fact, minimal - we are talking about fractions of a degree. However, a characteristic pattern in which the temperature “dives” down and then quickly “climbs” to new heights makes it possible to detect ovulation. This means preparing for the long-awaited conception.
How is basal temperature measured during preparation for pregnancy?
We will not give you false hopes and tell you that this is an easy task. Not at all: it requires high discipline, attentiveness and strict adherence to the rules. We are talking about the need to detect almost imperceptible fluctuations of a fraction of a degree, and any error in measurements can become critical. It's best if you get training from your doctor, but we'll also give you a guide with 10 main principles for measuring basal temperature in preparation for and in early pregnancy.
- Only a very accurate thermometer is suitable for measurement. It is best if it is a modern digital device. Read the operating instructions carefully and do not forget to change the batteries in a timely manner. The thermometer cannot be changed during the menstrual cycle - individual errors of different devices can distort the picture.
- Measurements are best taken in the rectum. Measurements in the vagina or mouth are acceptable, but the rectal method is considered to be the most reliable. Whatever method you choose, do not change it during the cycle. Armpit measurements are not suitable for tracking ovulation because they do not provide the necessary accuracy.
- Measurements are taken only in the morning, immediately after waking up. You cannot get out of bed or make sudden movements; even a short trip to get a thermometer and back to the other end of the room can ruin everything. Prepare a thermometer the night before and place it so that it is at arm's length.
- To avoid spoiling the readings, lie still and do not change your position. Try to do everything to prevent the brain, and after it the body, from switching to “work speed” - do not think about plans for the day, about important matters and problems. Ideally, don't even open your eyes.
- Basal temperature should be measured every day at approximately the same time. A schedule in which you get up, for example, at 6 am on weekdays, and at 10 am on Saturday and Sunday, is not suitable. To ensure the necessary accuracy, you will have to set the alarm clock at 6 a.m. on weekends, or at most 7 a.m.

- The measurement should be taken after 3 or more hours of restful sleep. Try to eliminate all factors that can interrupt your sleep, in particular, do not drink a lot of fluids in the evening so that you do not have the urge to go to the toilet at night. If you slept less than 3 hours, the result may be significantly distorted.
- Measuring your basal temperature during the day when preparing for pregnancy is only possible in extreme cases, for example, if you work night shifts. Before this, you need to sleep at least 3 hours. And, of course, if you are planning to get pregnant, you need to change your work schedule or move to another job.
- Once the measurements are completed, immediately write down the result. Don't rely on memory - in the time it takes to visit the toilet or put on the kettle, the brain can switch to some important thought, and the numbers will fly out of your head. It is best to record measurements electronically. Microsoft Excel or another similar program will allow you to automatically draw a basal chart in preparation for pregnancy, which is much more visual than just a column of numbers on a piece of paper.
- Please make comments about any unexpected deviations in measurements. If you understand what led to them, write down the reason. This could be a slight illness, alcohol, sex before bed, taking certain medications, stressful conditions, severe physical activity and some other factors.
- If you catch ARVI, flu or another disease that causes your body temperature to rise significantly, feel free to stop taking measurements. While the immune system is fighting the disease, you will not see anything useful on the chart. Also, measurements are absolutely meaningless when taking oral contraceptives.

Why measure
The main purpose of measuring basal temperature is to assess a woman’s hormonal status, which may be needed in the following situations:
- Natural contraception. A woman identifies the fertile phase of the cycle, that is, the most dangerous days when conception is most likely. This is how she plans her abstinence days. Suitable for couples who do not want or cannot use other methods of protection.
- Pregnancy planning. A woman also identifies favorable days for conception - a couple of days before and during ovulation.
- Identifying the cause of infertility. The measurement and its results are used in combination with other methods and help determine cycle disorders, the presence or absence of ovulation (anovulatory cycles). By the way, normally there can also be anovulatory cycles, but they occur more than 1–2 times a year.
- Diagnosis of pregnancy.
How to measure basal temperature during pregnancy?
In exactly the same way as when planning a pregnancy. It is advisable that you use the same thermometer - if it “lies” a little, at least the readings will be overestimated or underestimated in the same direction as before.
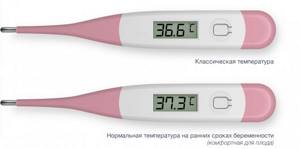
The temperature chart during pregnancy is, in fact, nothing interesting. The most comfortable temperature for fetal development is 37.0–37.3 °C, and your body will try to maintain it throughout the entire period of gestation. Basal temperature in pregnant women can change significantly only in case of pathologies, for example, with a frozen pregnancy or a threat of miscarriage. However, in such situations, the body lets you know that something has gone wrong with nagging pain in the lower abdomen or bleeding. In this case, you should not wait until the morning to take measurements: any dangerous symptoms are a reason to immediately contact your doctor.

What should a basal schedule look like when preparing for pregnancy?
Describing how basal temperature changes during the menstrual cycle is useful information, but can be difficult to understand without specific examples. So let's look at some graphs that visually show what measurements you can get.
Normal menstrual cycle
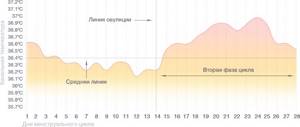
Normal menstrual cycle schedule
During the normal course of the menstrual cycle, you can see two different phases on the graph - in the first, the average level of basal temperature is lower than in the second, and ovulation serves as their boundary. It is not necessary that your schedule is divided into two equal parts of 14 days, as in this example. The duration of the second phase of the cycle for different women can be from 12 to 16 days, and the first can vary within even wider limits. There is nothing unusual in this, just the individual characteristics of the body. However, different cycles of a particular woman should follow the same scenario. After a couple of months of measurements, you will already roughly understand what day of the cycle ovulation should occur.
This graph gives an understanding of what basal temperature is normally observed in preparation for pregnancy. In the second phase it should be 0.3–0.6 °C higher than the average level of the first period. At the same time, a drop in the temperature curve is observed at the end of the cycle, before the onset of menstruation. And, of course, the preovulatory drop followed by a rise is important for the expectant mother.
Anovulatory cycle
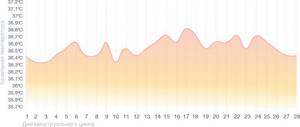
Anovulatory cycle chart
In the anovulatory cycle, ovulation does not occur, and hormonal levels change slightly. Throughout the entire cycle, the basal temperature remains almost at the same level - around 36.6 ° C, and the graph does not show pronounced phases and drops that are observed in a normal menstrual cycle.
If your temperature curve looks like this in the first month of measurements, there is no need to panic. Every woman has one anovulatory cycle per year, sometimes more. It’s just that your reproductive system periodically needs rest, and it arranges it for itself during periods during which it is impossible to get pregnant. However, if such a picture is observed for more than two months in a row, you need to consult a doctor - this is no longer a rest, but a possible sign of infertility.
Hormonal problems
Let's look at what a basal temperature graph might look like for various hormonal disorders.
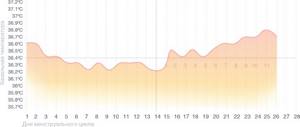
Diagram for corpus luteum deficiency
The corpus luteum forms after ovulation and produces progesterone, which is necessary to prepare the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg. If the corpus luteum produces little progesterone, an already begun pregnancy may be terminated.
This condition can be calculated by the slow rise in temperature in the second phase, and for its treatment the doctor will prescribe hormonal drugs.
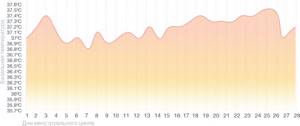
Schedule for estrogen deficiency
If a high level of progesterone leads to an increase in basal temperature, then an increase in estrogen production leads to a decrease in it. It is thanks to them that the temperature drops before ovulation. With estrogen deficiency, the likelihood of fertilization decreases significantly.
This condition can be identified by an unexpectedly high temperature at the beginning of the cycle, a slow increase in the middle, and a temperature above normal for the second phase. It will not be possible to detect ovulation using such a schedule. In case of estrogen deficiency, hormonal medications are also prescribed.
Pregnancy
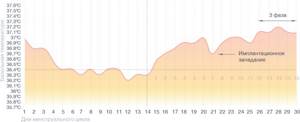
Schedule during pregnancy
You determined the day of ovulation using measurements, you have already had that same sex. Keep monitoring - you may soon be able to detect pregnancy even before the test shows two lines!
In early pregnancy, basal temperature drops on the day when the egg implants. The characteristic implantation retraction divides the second phase into two, and a third phase appears in your chart, indicating that pregnancy has begun. It is worth remembering possible inaccuracies in measurements and it is better to wait until your doctor confirms this joyful fact. But, most likely, you can already be congratulated - you have begun your journey to becoming the best mother to the best baby in the world!
Basal temperature chart - definition of pregnancy, signs of pregnancy.
There are a number of pregnancy signs that can confirm that you are pregnant. Along with the absence of menstruation, this includes nausea in the morning, swelling of the mammary glands and excessive drowsiness. Another sign of pregnancy is increased irritability; previously familiar things may start to piss you off. Signs of pregnancy are an increase in appetite and the appearance of so-called “taste perversions,” that is, a sharp desire to eat pickled cucumber jam. Signs of pregnancy - night trips to the toilet become more frequent, and even during the day long walks can become problematic due to the frequent urge to urinate. However, all these are indirect signs of pregnancy, and they may not exist, and sometimes, on the contrary, indirect signs of pregnancy are obvious, but there is no pregnancy. Rules for measuring basal temperature Basal temperature is measured daily, without interruptions for menstruation, illness, holidays, etc. for at least 3 menstrual cycles. Of course, measuring basal temperature can be of a specific nature (for example, for diagnosing early pregnancy), and therefore be episodic, over several days. The measurement time should be the same throughout the entire examination; the time difference should not exceed 30 minutes. Having woken up, the woman does not get out of bed and does not make sudden movements. He takes a thermometer and carefully inserts the narrow part into the anus. The measurement can last from 5 to 10 minutes, but the measurement time should be approximately the same all the time. Removing the thermometer, the woman immediately writes down the readings, and then wipes it, shakes off the column of mercury, and puts it back until the next measurement. Special conditions for measuring basal temperature: When measuring basal temperature, it is necessary to pay attention to external and internal circumstances that may affect the indicator. Such situations include: diseases with a general increase in temperature, local inflammatory processes (acute hemorrhoids and rectal fissure), diarrhea, exacerbation of adnexitis, copious vaginal discharge, abscesses or boils of the buttocks, inflamed wounds on the legs. External reasons may be: measuring basal temperature at an unusual time, short sleep time (less than 5 hours before the measurement), active intercourse the night before or sexual intercourse in the morning, masturbation less than 3-4 hours before measurement, drinking alcohol the day before , sleeping in unusual temperature conditions (too cold or too hot), using an unusual thermometer, taking some medications (specify which ones). All these points must be noted on the basal temperature recording sheet. If the basal temperature goes beyond the logically expected range (too high or too low), it is necessary to note the probable cause in the “NB” column of the chart (see below). This is necessary so that later, when analyzing the dynamics of basal temperature, it is possible to distinguish such random deviations from painful ones. In some cases, such a difference can be decisive when discussing the causes of infertility and further treatment. In addition, the basal temperature table indicates days of unprotected intercourse. How to keep records of basal temperature measurements. You can make rough notes of basal temperature on a separate sheet, and then, after understanding the results, transfer them to the main sheet with the graph. In this case, the draft has only three columns: cycle day (dc), basal temperature, special marks (NB). This form of recording a basal temperature graph looks like this: Cycle day 1 2 3 4 5 BT 37.1 37.0 36.8 37.3 37.2 NB flu? In the future, the presence of influenza or another disease may be confirmed, and the entry in the NB column will remain. If the diagnosis is not confirmed, then the condition is at 4 and 5 d.c. may give rise to serious consideration of the presence of endometritis. But you can record directly on the main sheet, which includes a graph of basal temperature and a recording table (with footnotes about treatment and sex life). A graph of basal temperature is drawn on a sheet of paper with a checkered pattern. One basal temperature chart should include data from the 1st day of your period until the last day before your next period. If the cycle is too long, a second sheet is glued in width. You can place two basal temperature graphs on one sheet (one below the other), but it is better to take a separate sheet for each cycle, and draw the basal temperature graphs only on one side so that they can be laid out for comparison, rather than turning the sheets over, looking for the next cycle . There is no need to place data from 2-3 or more cycles on one basal temperature chart, marking them with different colors, and even more so, with different types of dotted lines. This will only make basal temperature charts more difficult to read without providing any further comparison between different cycles. The scale of the basal temperature graph: 1 cell in height corresponds to 0.1 * C, 1 cell in width corresponds to 1 day. The temperature scale averages a column from 36.3 to 37.4, although the final marking is made only after the end of the cycle. At the level of 37.0, a thick horizontal line is drawn, which allows you to better navigate the indicators. On this line you can mark the days of menstruation, as well as the abundance of discharge. After all the values are plotted on the sheet, the points are connected by a continuous line. Directly below the basal temperature chart there is a table with all its features. Below the table, in any form or again in the form of some kind of table, is additional information: intercourse, taking medications to combat infertility, etc. In its final form, the basal temperature measurement sheet has the following form: Temperature 37.4 37.3 37.2 37.1 O 37.0 O O 36.9 O 36.8 36.7 O 36.6 O 36.5 36, 4 O 36.3 O O 36.2 O Day of the month 29.3 30.3 31.3 1.4 2.4 3.4 4.4 5.4 6.4 7.4 Day of the cycle 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Basal temperature 37.1 37.0 37.0 36.9 36 ,7 36.6 36.3 36.3 36.4 36.2 NB Mens.(3) Mens.(4) Mens.(5) Mens.(3) Mens.(1) Slept little Additional information In addition to everything described , on a sheet with a basal temperature graph, you can mark everything that you consider important, as well as what you are afraid to forget (and you will probably forget if the basal temperature measurements continue for more than a few months). It is quite difficult to correctly decipher the temperature curve, which is very important. Remember the following: * Basal temperature decreases 12-24 hours before ovulation, and after ovulation it increases by an average of 0.2-0.5 degrees. * Thus, the period from the beginning of the menstrual cycle until the basal temperature is increased for 3 consecutive days is considered fertile (since the egg loses its ability to fertilize 3 days after ovulation and pregnancy is impossible) * Since the basal temperature reacts to various factors, the interpretation of basal temperature readings requires special attention. Therefore, it makes sense to make special notes about these factors. These include: illness with an increase in temperature (fever), drinking alcohol the night before, stress, sleepless night. So, if you have had insomnia, specifically note this fact. The greatest difficulty for women is the correct interpretation of the resulting temperature graph. As mentioned above, the schedule allows you to determine the day of ovulation. How to determine the moment of ovulation In order to determine this, carefully study your chart and pay attention to the following facts: * Find the day when the temperature increased by 0.2 - 0.5 degrees higher than in the previous 6 days. For convenience, mark these previous 6 days in a different color. * Select the highest of these 6 temperatures and draw a horizontal line 0.1 degrees above it. * Most likely, temperatures lying above the horizontal line will lie above the horizontal line. They reflect the days when ovulation has already occurred. If suddenly the temperature on one of the following days drops below the horizontal line, you need to wait again for a rise above it. * Count 4 days of high temperatures above the horizontal line and draw a vertical line. These are the days when you are unable to conceive. * If suddenly a day with an unexpectedly high or low temperature appears on the basal temperature chart, then do not take this temperature into account when finding 6 days. You are unable to conceive: * The first 5 days of the menstrual cycle, if the week before there was a noticeable rise in temperature. It doesn't matter when your period ends. (This is true for cycles longer than 25 days). If you have shorter cycles, then the inability to fertilize will only be the first 3 days. The fact is that with a short cycle, the likelihood of ovulation increases, which will occur earlier. If you are approaching menopause, then this rule does not work, since early ovulation is more than possible. * If you have a high temperature for three days, then you are unable to conceive from the evening of the third day before the start of menstruation.
Program for pregnancy management and preparation for childbirth.