Estrogen production process
Estrogen synthesis is impossible without its precursors: testosterone and androstenedione
. This all happens under the control of the aromatase enzyme. If the process of estrogen production is affected by any genetic defects of the enzyme, then an increase in the level of male hormones is possible.
Estrogen production is impossible without androgen synthesis, which occurs due to cholesterol. That is why women who follow a cholesterol-free diet face unpleasant consequences in the form of hormonal problems.
As already noted, the synthesis of estrogens is impossible without its assistants, because:
- estrone is produced from androstenedione;
- estradiol is produced from testosterone;
- Estriol is produced from estrone in the blood.
Function of estrogen
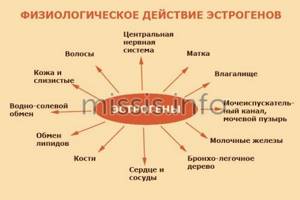
The active action of estrogen begins after binding to the corresponding receptors. The hormone is responsible not only for exclusively female functions, it has a complex effect on the entire body. The period of menopause, when estrogen levels drop sharply, is associated with a deterioration in a woman's health. This is because the hormone has been protecting the body from pathological processes all this time.
Menopause can provoke heart disease, atherosclerosis, and diseases of the reproductive system.
The main function of the hormone estrogen, which is responsible for in women:
- stimulating the development of the uterus, appendages, mammary glands and vagina;
- determination of secondary female sexual characteristics;
- regulation of bone growth;
- menstruation, when the inner layer of the uterus is shed;
- regulation of blood clotting;
- protection of blood vessels from cholesterol plaques;
- control of antithrombin, a substance that breaks down blood clots;
- increased affinity for progesterone, infertility and miscarriage are possible even with normal levels of progesterone, provided there is insufficient production of estradiol.
[media=
https://youtu.be/Xl56b_hZVFU
]
The role of estrogen in the body
So, what is this hormone in women - estrogen? It would be more correct to say that this is a whole subclass of steroid female sex hormones, most of which are produced by the follicular apparatus of the ovaries. There are three types of estrogens: estradiol, estrone and estriol. Despite the fact that estrogen is called a female hormone, it is also found in the body of men.
However, in the fair sex this hormone is produced in much larger quantities, and estrogen has a much stronger effect on a woman’s body than on a man’s body. What is the hormone estrogen responsible for in women? It performs several important tasks at once:
- Participates in the formation of primary female sexual characteristics. Estrogen promotes the development of the vagina, stroma and ductal systems of the mammary glands, and also stimulates the development of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Ensures the functioning of the reproductive system. It is thanks to the hormone estrogen that the endometrium is regularly rejected from the uterus and, as a result, menstruation occurs.

- Takes part in the functioning of the circulatory system. Estrogen helps increase plasma levels of high-density lipoproteins, which reduce the risk of all kinds of cardiovascular diseases and atherosclerosis. At the same time, this hormone reduces the concentration of low-density lipoproteins, which carry cholesterol. In addition, the female hormone estrogen increases the levels of copper, thyroxine and iron in the blood.
- Plays an important role for the skeletal system. Estrogen in the body prevents calcium from being washed away, protects joint tissue and stimulates the repair of bone cells.
- Estrogen helps maintain skin elasticity by stimulating collagen production.

Estrogens and breast cancer - relationship and prevention
Breast cancer is a serious disease, which also depends on the level of estrogen. They also often talk about estrogen metabolites and their ratio. Without medical education it is difficult to understand this. We asked the experts of the New Life project to answer the most frequently asked questions in simple and understandable language (as far as possible). After reading this article, you will learn what estrogens and their metabolites are, how they are related to women’s health and many other equally important things.
- Let's first figure out what estrogens are and why they are needed.
Estrogens are hormones. So let's start with what hormones are in general. These are substances with which the body sends signals to itself. For example, growth hormone tells some cells in the body to grow; adrenaline tells them to go on alert. It's easy to get confused about hormones because each of them has several functions.
Estrogens are sex hormones. They are called so because they mainly act on the woman’s reproductive system, that is, on those organs that are needed for pregnancy, childbirth and feeding. For example, estrogens help organize the menstrual cycle so that a woman is ready to conceive. Women have much more estrogen than men. Strictly speaking, it is estrogens that make a woman’s body female.
Estrogens have other functions as well. For example, they support bone health, affect mood, cholesterol levels, heart and vascular function, and even a little on skin condition. Every doctor who deals with women's health should have at least a little understanding of estrogens. Most often, estrogen tests are prescribed by gynecologists. A competent doctor is not interested in the hormone itself, but in the entire system in which it works.
— Is it true that there are different types of estrogens and that they also work differently in the body?
Yes, estrogens are a collective name for several hormones. The three most important are estrone, estradiol and estriol. They differ from each other in structure and slightly in their task. Estradiol is the most important and most famous. It organizes the menstrual cycle and supports women's health until the last menstruation. After this, estrone becomes the main one, although there is less of it in the body. Therefore, sometimes doctors after 50 years give a woman small doses of estradiol to make her feel better. As for estriol, it is most active during pregnancy.
— What are estrogen metabolites and why are they important?
In nature, nothing disappears without a trace. After the hormone has entered the cell and told it what to do, it needs to be put somewhere. Otherwise, it will continue to give signals, and the cell will become confused. Therefore, the cell has a special system that takes estrogen and changes its structure. This process is called estrogen metabolism, and the resulting new molecules are estrogen metabolites. They are needed to remove used estrogens from the body. If they were not there, estrogens would accumulate in the body, and this is harmful.
— They say that there are different metabolites. What is the difference?
First, a few words about how estrogen metabolism works. This is a complex chain of chemical reactions. It can be compared to a chemical factory. The input is estrogens, the output is metabolites. And in this factory there are three conveyors. Depending on which conveyor belt estrogen gets into, one or another metabolite will be obtained. To avoid confusion, doctors and chemists use the numbers 2, 4 and 16. We can say that they indicate which conveyor the estrogen passed through. For example, 2-hydroxyestrone and 2-hydroxyestradiol are different molecules, but both are produced on the same assembly line. But 16-alpha-hydroxyestrone or 4-hydroxyestradiol are already products of other conveyors.
This is important because metabolites from different conveyors have different chemical properties. To avoid confusion, let's say this: 2-metabolites weaken the estrogen signal, while 4-metabolites and 16-metabolites give the same signal as estrogens or even stronger. Therefore, if a woman has risk factors for cancer, then 2-metabolites are beneficial for her, and 16-metabolites are harmful. Therefore, doctors are interested in the ratio of 2-metabolites and 16-metabolites. If there are more 2-metabolites, then it will be more difficult for estrogens to make the cell grow. And if there are more 16-metabolites, then it will grow stronger. As for the 4-metabolites, they act differently, and we will not go into them in detail.
Doctors try to suppress the estrogen signal to prevent tumor cells from growing. For example, tamoxifen is prescribed for this - it prevents estrogens from stimulating cell growth. But tamoxifen has side effects because it turns off all estrogen signals, both good and bad. So doctors have come up with other ways to influence the estrogen signal. If you make sure that the factory we talked about produces more safe 2-metabolites and fewer harmful 16-metabolites, then it will be easier for the body to fight the tumor or prevent it from arising.
— How then can we understand how many and what metabolites are produced?
This is precisely why an analysis for estrogen metabolites is needed. Usually, when we do a test, the laboratory gives us the results with a label that lists the different metabolites and their levels. It looks something like this:
| Metabolite | Name | Level | Norm |
| 2-OHE1 | 2-hydroxyestrone | 2,69 | 0,24-11,1 |
| 2-OHE2 | 2-hydroxyestrone | 6,32 | 0,35-10,77 |
| 16a-OHE1 | 6-alphahydroxyestrone | 2,986 | 0,079-4,070 |
When we receive the analysis, we immediately look to see if our levels fall within the normal range. This plate shows that all metabolites seem to be within normal limits. But it’s too early to rejoice, because we are not interested in the metabolites themselves, but in their ratio. We need to understand which metabolites are more numerous, and for this we need to divide the good ones into the bad ones. Usually the laboratory does this itself. For example, the analysis form may contain the following line:
(2-OHE1 + 2-OHE2) / 16a-OHE1 = 3.02
Let's figure out what is what. In the first part, before the division sign we have brackets. In these brackets there are two different metabolites. By the number “2” in the name, we understand that these are useful 2-metabolites. After the division sign we have a dangerous 16-metabolite. All this means is that the laboratory looked at the level of each metabolite, and then divided the 2-metabolites into 16-metabolites. And the result was 3.05.
To make it clearer, let's see what it looks like with numbers:
2,69 + 6,32 / 2,986 = 3,02
It turns out that this woman has a metabolite ratio of 3.02. It remains to be seen whether this is good or not. Doctors have a simple rule for this. If the ratio is greater than 2, it means there are twice as many good metabolites, which is good. If the ratio is less than 2, then it is not very good. In general, the higher the ratio, the better. The lower, the worse. For example, in another woman we get the following results:
1,09 + 2,13 / 4,49 = 0,71
A result of 0.71 means that the ratio is low, meaning that there are many more dangerous 16-metabolites. This means that cells receive a signal to grow, and the risk of various diseases is increased. Something needs to be done, and we'll talk about it a little later.
— What test is best to take for estrogen metabolites?
Estrogen metabolites are usually found in urine. Sometimes in a single portion, sometimes in a daily dose. If possible, it is better to do it on a daily basis, because then we get a more accurate picture.
— How to prepare for research?
No special preparation is needed. If you are giving a single urine sample, you need to collect the middle portion in the morning in a sterile container (they will give it to you in the laboratory or sell it at the pharmacy). The average portion means that you need to start urinating in the toilet, then place the container under the stream and then remove it.
If you donate daily urine, then everything is a little more complicated. In the laboratory you will be given two containers - a large and a small one. The day you start collecting urine, you urinate in the toilet in the morning because the first daily amount is not counted. Then, for 24 hours, you urinate only in a large container, even if you wake up during the night. It should be stored in the refrigerator on the bottom shelf (temperature from 2 to 8 degrees, cannot be frozen). The next morning, you also urinate into a container, and then measure the volume of urine (there are measuring divisions on the container) and then mix the urine thoroughly, pour 50-100 ml into a small container, and take it to the laboratory within an hour. On a small container you need to write how much urine you collected.
There are a few more rules: during urine collection, you drink and eat as usual, do not drink alcohol, try to refrain from physical activity, and do not take diuretics. If all this is done, the analysis will be more accurate.
— Who is this study for?
It can be done to any woman who has risk factors for cancer and some other problems. The most common of them are obesity, irregular menstrual cycle, and various types of ovarian dysfunction. And of course, any problems with the mammary gland. Analysis of the ratio of metabolites does not replace other tests (for example, for genetic predisposition to cancer). But it helps to plan prevention more effectively and see how it works. — What will this analysis give, what will it help?
Let's imagine this situation. There is a woman who is 55 years old. Several years ago, she was diagnosed with breast cancer, had surgery and a course of therapy. Now she seems to be in no danger. But the doctor decides to check how high the risk of relapse is. To do this, the woman does an analysis of the ratio of metabolites, and it turns out that it is very low. This means the risk is increased. The doctor gives her recommendations for prevention and asks her to take the test again in six months. The woman follows all the recommendations and on repeated analysis sees that the ratio of metabolites has increased. This means that the risk has decreased. So now she definitely won’t get sick?
Unfortunately, there is always a risk. Cancer is a serious disease, and no one can give complete guarantee that it will not occur or that there will be no recurrence. But prevention is still needed. Let's look at this from a different perspective. When a person drives a car, there is always a risk of getting into an accident and getting hurt. But this risk varies. If the driver is careful and knows the rules well, the car is reliable and undergoes maintenance every year, and the road is clean and safe, then the risk is very low. But if the driver is drunk, the car smokes and creaks, and there is ice and fog on the road, then the risk is very high. Therefore, all we can do is to reduce the risk by all means.
— Let's talk about prevention.
There are two types of breast cancer prevention. The first is chemoprophylaxis, that is, various drugs that reduce the activity of the estrogen signal. They must be prescribed by a doctor. The second is a healthy lifestyle. Doctors recommend not smoking, moving more, and eating healthy food. These are universal recommendations, but they are especially important for women. The fact is that proper nutrition provides the necessary resources for the proper functioning of our metabolite factory. That is, if a woman eats better, then she has more beneficial metabolites and fewer dangerous ones.
— What foods are recommended to eat to improve estrogen metabolism?
Research in recent years has shown that plants from the cruciferous family are best suited for this role. We are talking about broccoli, cauliflower and zucchini. In the process of evolution, they learned to synthesize a substance called indole-3-carbinol. It helps our internal factory work better and produce more beneficial metabolites. As a result, the metabolite ratio increases and the risk decreases.
similar on topic
Cancer protection: what women need to know about indole-3-carbinol
READ MORE
A large European study compared people who ate cruciferous vegetables regularly with those who ate them rarely or not at all. It turned out that cruciferous vegetables can reduce the likelihood of breast cancer by 17%. This is not very much from a statistical point of view, but for specific women who do not develop breast cancer, this is a good result.
“Many people will now ask: is it really necessary to eat broccoli or cauliflower every day now?”
It’s possible, but, firstly, not everyone likes broccoli, and secondly, some of the beneficial substances are destroyed during heat treatment. Therefore, it is easier to take a dietary supplement that already contains indole-3-carbinol. For example, in Russia there is a dietary supplement called Promisan. Promisan contains the dose of indole-3-carbinol necessary for prevention, as well as several other useful substances - green tea extract (helps fight inflammatory processes) and vitamins. Promisan is taken twice a day, two capsules, simultaneously with meals, for 3-6 months. Combined with regular physical activity and weight loss, this can give good results. And to evaluate it, we need estrogen metabolites.
Let's look at it with an example. Let's say there is a woman who wants to reduce the risk of breast cancer or recurrence. She takes tests for estrogen metabolites and begins to engage in prevention: she takes indole-3-carbinol, tries to move more, and tries to quit smoking. Six months later, she takes the test and looks again at what happened. If she did everything right, then the ratio should increase. For example, it was 1.5, but became 4.2. This means that there are more beneficial 2-metabolites, and therefore the risk has decreased. This is a good scenario, but what could go wrong? Yes, life happens differently. Let's look at other scenarios.
- If she has not been examined before and then finds out that she has a low metabolite ratio, then she should consult a doctor. What if she already has some kind of disease? And then prevention is still needed, because it is useful in any case;
- If she gets tested and the ratio is greater than 2, then the risk is not very high. But prevention still won't hurt. As we remember, you should always try to reduce the risk;
- If, after six months of prevention, she took a second test, and the ratio of metabolites did not increase, then most likely prevention through lifestyle is not enough. In such a situation, you should consult a doctor so that he can decide whether chemical prophylaxis is needed.
— Can Promisan be combined with chemotherapy for breast cancer?
Yes, you can, it does not interfere with other medications (daunorubicin, paclitaxel, doxorubicin and others). But if you are seeing a doctor and receiving chemotherapy, you still need to consult a doctor.
— Why Promisan, and not other indole-3-carbinol preparations, which are cheaper?
Because, unlike most dietary supplements, Promisan is made following all necessary technological procedures. When buying Promisan, you pay for two things: high-quality raw materials and the correct production technology. If you are offered to buy “the same thing, but cheaper,” this means that the manufacturer either saved on raw materials or saved on production. As a result, this always saves on your health. I would also like to note that Promisan has been clinically tested, which is difficult to find in other dietary supplements.
And remember that treatment and prevention are two different things. The treatment is carried out by a doctor, for this he can prescribe medication or perform surgery. But prevention is the patient’s task; the doctor here can only give advice. The doctor can remove the tumor, but cannot eat healthy food (or take dietary supplements) or move more for the patient every day.
PHOTOS: unsplash.com
Share
What are the dangers of hormone deficiency?
Women often have to deal with symptoms such as hair loss and brittleness, dry skin, mood swings, insomnia, headaches, decreased sex drive, engorgement and pain in the mammary glands. As a result of numerous attempts to identify the cause, long visits to various specialists begin. And they end with a gynecologist, who, having noticed such symptoms, immediately directs the patient to take tests for hormones.
Estrogen is not a single hormone, but a class of compounds that have similar properties.
Estrogens are present in both humans and animals. In humans, there are three of them: estradiol, estrone and estriol. The leading role of estrogen is to control functions related to the functionality of the uterus. The hormone promotes the growth of the endometrium. Consequently, estrogen is a growth hormone, so its increased content in the blood can lead to various diseases, including dangerous ones. For example, hormone-dependent pathologies include:
- allergy;

- endometriosis;
- fibrocystic mastopathy;
- endometrial and breast cancer, etc.
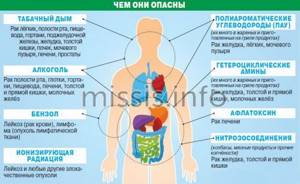
The level of zinc and magnesium in the blood, the most important elements responsible for the condition of the skin and muscles, may also decrease. Possible decrease in mental abilities and weight gain. Excess estrogen is processed by the liver, the diseased organ cannot cope with the load and the excess hormone remains in the body. Therefore, if you have a weakened liver, use a large amount of medications, alcohol, or have an unhealthy diet, checking your estrogen level is a must.

High estrogen in women: what is the reason?
Experts still cannot articulate the specific reasons for high estrogen.
Among the factors that provoke excess emissions:
- benign and malignant ovarian tumors;
- pathological processes in the adrenal glands;
- neoplasms of various types;
- pituitary adenoma;
- age-related changes, including menopause.
In addition, estrogen levels can be affected by an unbalanced diet, smoking, alcohol abuse, irregular sexual relations, chronic diseases of the reproductive system, and regular nervous strain.
In many cases, an excess of the hormone is provoked not by one factor, but by a combination of them. Signs of high estrogen in women can be caused by a number of other medical conditions. There is no point in diagnosing yourself. Only a specialist, after examination and tests, will be able to determine the reasons for the patient’s poor health.

At the first signs of hormonal imbalance, you should immediately consult a specialist.
At the first symptoms of an increased level of estrogen in the body, a woman should undergo a full examination by highly specialized specialists, which will help to quickly prescribe the most effective treatment.
If you suspect you have a hormonal imbalance (lack or excess of some hormones), first of all, you need to contact a specialist - a gynecologist or endocrinologist.
Symptoms of insufficient hormone production
Cause of estrogen deficiency
- insufficient production by the ovaries. This is possible due to age-related changes or initial problems with the pituitary gland, a glandular organ that stimulates the production of sex hormones.
Another reason is an excess of testosterone, a male hormone that is normally present in the female body in small quantities.
Lack of estrogen in women. Symptoms of pathology during menopause:
- Deterioration of the condition of the skin. Dryness and flaking appear, the risk of injury increases, and elasticity decreases.

- Temperature changes, the woman becomes either hot or sharply cold. This condition occurs as a consequence of changes in blood pressure.
- The strength of bones decreases, even a minor bruise leads to a fracture and prolonged healing.
- Problems appear in the functioning of the heart.
Clinical picture at a young and mature age:
- A young body reacts to hormone deficiency differently. The girl has delayed sexual development.

- Secondary sexual characteristics develop poorly or do not develop at all.
- Menstruation begins much later than among peers.
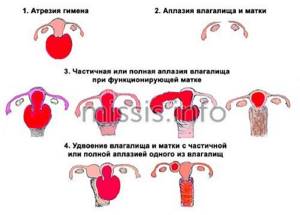
- Increased body hair.
- Problems that arise in an already mature woman look different. Menstrual irregularities occur.
- Breasts become smaller.
- The condition of the skin worsens, early wrinkles appear.
- There is vaginal dryness.

- Infertility.
The inability to get pregnant forces a woman to undergo a comprehensive examination, which reveals a deficiency of certain hormones.
Estrogen deficiency provokes the following pathological conditions:
- myocardial infarction;
- uterine prolapse;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract;
- diabetes.
What are estrogens, their norm and importance for the body
A group of female sex hormones that are synthesized in a woman’s body by the ovaries and regulate specific sexual functions are called estrogens. This main type of female hormone ensures, during adolescence, the development and formation of secondary sexual characteristics in girls.
At a more mature age, estrogens take an active part in the formation of the female reproductive system, preparation for pregnancy, ensure the timely release of the egg into the genital tract and fertilization after ovulation, contribute to the natural hydration of the vaginal mucous tissues and the preservation of its favorable microflora.
Estrogens in the body work in tandem with progesterone and together ensure the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy, its safety and a favorable birth.
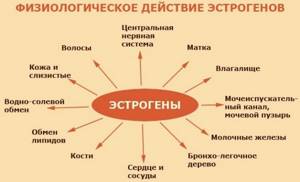
Normal estrogen levels have a beneficial effect on skin and hair. The level of cholesterol in the blood, the strength of bone tissue, good memory, the complete absorption of calcium, magnesium, potassium and the coordinated functioning of the whole organism depend on its optimal amount.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K08eMYPcei4
In other words, estrogen is a hormone of youth, responsible for a woman’s emotional state, her libido, attractiveness and sexuality.
The body produces three types of estrogens:
- estriol is a minor sex hormone, present in low concentrations, produced mainly during pregnancy;
- estradiol is the most active steroid hormone common in women of childbearing age;
- estrone is the only hormone that the body produces after the onset of menopause.
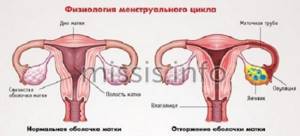
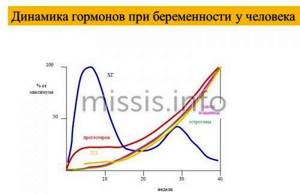
Hormones do not stand still; their levels can constantly change depending on the female cycle. In the first phase of follicle development, estrogen levels are at a fairly low level, but along with the production of a dominant follicle, there is a gradual increase in estrogen levels.
With full maturation and rupture of the follicle, during the release of the egg during ovulation, estrogen levels rise to their maximum value. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the amount of estrogen gradually decreases and drops to a minimum value.
The optimal fluctuations in estrogen levels in a healthy woman are:
| Cycle phase | Period of the phase | Phase duration | Hormone level, pg/ml |
| Follicular | First day of menstruation | from 7 to 22 days | from 57 to 227 pg/ml |
| Periovulatory | period before and after ovulation | 2-3 days | from 127 to 476 pg/ml |
| Corpus luteum phase (luteal) | after ovulation | 12-14 days | from 77 to 227 pg/ml |
| Menopause | from 19.7 to 82 pg/ml |
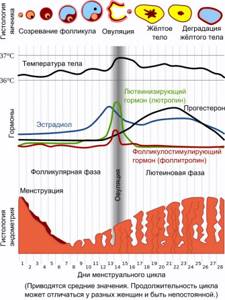
As we age, hormone levels decrease significantly. After the onset of menopause and menopause, its amount decreases by 40 - 60%. Estrogens are naturally occurring hormones important for sexual development and other body functions. Before menopause they are produced mainly in the ovaries, after menopause they are produced in adipose tissue.
When working stable, estrogen is in balance with other hormones, but sometimes, under the influence of certain factors, its level can increase and begin to prevail over progesterone, which can lead to serious disruptions in certain body functions.
Symptoms of excess hormones
Estrogen dominance is indicated when the concentration of the hormone in the blood exceeds the permissible values.
Excess estrogen in women, symptoms:
- migraine and frequent headaches;
- swelling of the limbs and face;
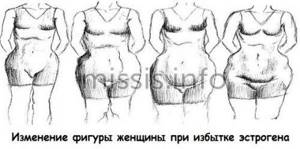
- increased blood pressure;
- decreased sexual desire;
- the appearance of cysts in the ovaries and breasts;
- lack of pregnancy due to the impossibility of egg implantation;
- hair loss;
- the appearance of acne on the face;

- the appearance of spotting in the middle of the cycle;
- decrease in days of menstruation.
Excessive amounts of estrogen
negatively affects the functioning of the reproductive system. It disrupts the usual course of hormonal fluctuations, which ensure the maturity of the egg, timely ovulation and, if pregnancy does not occur, rejection of the endometrial mucosa.
Excess estrogen is dangerous for women who are overweight. With menstruation, the endometrial mucosa comes out, but due to hormonal imbalances, it does not come out completely. This leads to the growth of the endometrium, which becomes the cause of precancerous diseases.
The development of cancer directly depends on excess weight, for example, in women weighing more than 80 kg, the incidence of malignant tumors is 10 times higher than in women weighing within the normal range.
How to get rid of excess estrogen?
The main thing is not to despair. An excess of the hormone estrogen in women, the symptoms of the disease in most cases are easily removable. In the early stages of hormonal imbalances, the internal forces of the body can easily cope with high estrogen. If this is not enough, medical intervention will be required to lower the level. After passing the tests, the specialist will prescribe medications that will help get rid of excess estrogen and normalize the condition. In addition, the woman will have to completely reconsider her lifestyle.
How to get tested?
In order to diagnose high estrogen in women, the symptoms and signs of which you have noticed in yourself, the specialist will issue a referral for a blood test, which is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach. It is not recommended to eat a lot the day before; it is better to limit yourself to light snacks. You should also have a good rest and not be nervous. These simple recommendations will help you get the most accurate results and understand whether estrogen is too high or the cause of the body’s malfunctions lies elsewhere.
Restoring the balance of hormones will improve the functioning of the entire body, and this guarantees good health, youth and attractiveness.

The sooner you see a doctor with your problem, the sooner you will return to a full life.
Causes of excess and deficiency of estrogens
There are several reasons for increased estrogen levels:
- early sexual development in girls;
- pregnancy - during this period a woman experiences an increased level of progesterone and estrogen, which are produced by the placenta and support pregnancy;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- adrenal tumors;
- use of countercurrent hormonal drugs;
- sedentary lifestyle, lack of even minimal physical activity;
- Deficiency of certain vitamins and minerals, such as folic acid and provitamin A.
Estrogen is called the hormone of youth
. From the moment of its sharp decline, the body begins to age. This is a normal condition at the time of menopause, but quite often, the drop in estrogen begins much earlier than the age of menopause.
- the whole body suffers from a lack of the hormone;
- memory deteriorates;
- mental activity decreases;
- the risk of atherosclerosis and hypertension increases;
- the skeletal system suffers;
- there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- the risk of malignancy increases.
To maintain health, a woman should listen to her body and undergo regular examinations to prevent the development of serious problems.
[media=
https://youtu.be/Y7ncRgygInQ
]
Natural Treatments
Elimination of serious hormonal disorders is carried out using hormone replacement therapy. However, many experts know how to increase estrogen in women in natural ways. First of all, it is recommended:
- pay attention to nutrition: add to the diet foods containing plant hormones with estrogenic activity;
- minimize carbohydrate intake;
- get rid of bad habits;
- include regular physical activity in your daily routine (any type of amateur sport is suitable: fitness, cycling, swimming);

- do yoga, meditation;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- try to replenish the deficiency of vitamin D in the body, spend more time in the sun;
- use folk remedies to raise estrogen levels.
Any treatment should begin only after a detailed examination and consultation with a specialist. Let's take a closer look at how to increase estrogen in women in natural ways, in particular nutrition. Nutritional therapy is an integral part of restoring hormonal balance. There are foods that can significantly increase the level of estrogen in the blood.

These are sesame, flaxseed, sunflower, beans, dried apricots and coffee. They are rich in phytoestrogens - plant-derived hormones that have a gentler effect on the body than synthetic ones. The use of drugs causes the ovaries to lose the ability to produce their own hormones.
Therefore, the best option would be to include the necessary products in the daily menu.
In many cases, correcting the diet and organizing a correct lifestyle is enough. This is an excellent way to regulate hormonal balance not only during menopause, but also after childbirth, when a sharp decrease in estrogen leads to the development of depressive conditions.

How to normalize hormonal levels?
How to treat excess estrogen in women? In order to improve hormonal levels and eliminate high levels of estrogen in women and symptoms, you will have to seriously take care of your health. Doctors recommend getting a good night's sleep, walking a lot in the fresh air, and trying not to get nervous. A good way to prevent hormonal imbalances is to exercise. In addition, it is worth paying attention to nutrition. Estrogen production is stimulated by soy, cheeses, yogurts, legumes, coffee and cabbage.
You can make an appointment with a specialist who, after examination and tests, will prescribe effective treatment now by following the link https://45plus.rf/registration/. A qualified specialist will analyze in detail excess estrogen in women, treatment, symptoms, and prescribe a number of recommendations or medications that are most suitable for you, taking into account all the characteristics of the body.
Treatment methods
For a certain period, a woman must take medications that will normalize hormonal levels. Selection of pharmacological forms to:
- compensate for the lack of estrogen, broad. Regular supply of female hormones can be ensured with the help of:
- gels (do not cause discomfort, there are no allergic reactions);
- plasters (convenient for women who work a lot and often travel on business trips);
- oral medications (easy to use, quickly increase the amount of female hormones);
- vaginal suppositories (have virtually no side effects);
- subcutaneous implants (valid for about six months, dosed release of hormones directly into the blood);
- intravenous and intramuscular injections (rapid increase in estrogen levels).
The pros and cons of using any of the options are determined by the individual characteristics of the woman and her preferences. Consultation with a doctor is required. Treatment regimens are different for women of different ages.
How to normalize hormone levels
{banner_banstat8}
Hormone replacement therapy is used to restore normal estrogen levels
. The same treatment is prescribed to a woman during menopause to eliminate the symptoms of menopause and maintain mental and physical health.
Your doctor may prescribe medications containing a synthetic hormone:
- proginova;
- Marvelon;
- silest;

- premarin;
- hemafin;
- rigevidon.
How to increase estrogen in women:
- Stop smoking.
- Engage in moderate physical activity regularly.
- Eat foods that increase estrogen production.

- Consume soy products, they alleviate the symptoms of menopause, but the hormone levels change only slightly.
- Don't overuse sugar.
- Include foods containing phytoestrogens in your diet. These include: peas, beans, apricots, prunes, some herbs such as oregano, sage, flaxseed oil, cauliflower and broccoli.
During pregnancy, estrogen levels increase tenfold. Do not use any medications or folk remedies during this period without consulting your gynecologist.
You should be careful with flax seed; excessive consumption reduces the effectiveness of some medications.

Excess and deficiency of estrogen have a detrimental effect on the condition of a woman’s body. But, the diagnosis can be confirmed only after laboratory testing. Do not delay visiting the clinic if you have some symptoms characteristic of hormonal imbalance. The sooner the problem is solved, the less harm it will cause to the body and the sooner it can be forgotten.
Reasons for increasing hormone levels
Hyperestrogenism is a pathology characterized by an increase in estrogen levels. It leads not only to hormonal imbalance, but also to malfunctions in many organs.
Why does the hormone level increase and hyperestrogenism develop?

There are certain reasons for this:
- Consumption of a number of products, most often dairy and meat. This is explained by the use of hormone-containing substances in animal breeding. Soybeans and legumes also contain plant estrogens.
- Illiterate distribution of loads (both high activity and inactivity).
- Alcohol, cigarettes.
- Coffee.
- Use of hormonal drugs.
- Lack and deficiency of vitamins.
- Precocious puberty (before seven years).
- Carrying a child. Vomiting in the first three months occurs precisely because of increased estrogen production.
- Irregularity of sexual activity.
- Stressful situations and depression.











