Correct and incorrect gait
With the correct gait, the spine is straight, the head, shoulders and pelvis are almost motionless, the arms move in rhythm with the walk. The body weight moves smoothly from foot to foot, the step width does not exceed two foot lengths. With each step, some muscles relax, others contract, alternating. In total, more than 200 muscles are involved in walking.
If the normal walking mechanism is disrupted, the desired muscle does not turn on in time, and its antagonist does not relax. Muscle imbalance occurs. As a result, muscle spasms, tension, pain appear, some muscles shorten and other muscles weaken. You can try to correct this imbalance with massages, a chiropractor or an osteopath, but the problem will quickly return. After all, after the session, you will again reproduce the same motor errors that brought you to a specialist.
Our tips and recommendations
Once correct posture has become habitual for you, you can begin exercises for correct gait:
- Place a book or a small pillow on your head and try to walk around the room with it, sit on the sofa, stand on one leg. Were you able to hold it? This means you have the correct position of your neck and head. If it doesn’t work out, practice.
- Walk in place without lifting your toes from the floor - this exercise develops your leg muscles well, which is very important for a beautiful gait.
- Imagine that your foot has a semicircular shape. Roll from heel to toe and back.
Install a floor-length mirror in the room, and walk for half an hour a day, observing your posture and the placement of your feet.
If you're ready to put on your heels and walk down the street in style, don't forget:
- Place your feet with your toes apart, otherwise your gait will be clubfoot.
- When placing the foot on the ground, the heel should touch it first (even if for a moment), and only then the entire foot.
- When transferring the center of gravity to the leg, it must be completely straight, otherwise walking “half-bent” cannot be avoided.
- To walk beautifully in heels, your legs must be strong and well-trained, so dance or join the gym.
By gait you can judge a person’s character and his state of mind at the moment. Stress, lack of self-confidence, and fear of appearing funny provoke slouching. Therefore, in order to walk correctly, you also need to think correctly . Remember the heroine of the film “The Most Charming and Attractive”? Convince yourself of your attractiveness, and your gait will instantly improve.
Some causes of abnormal gait
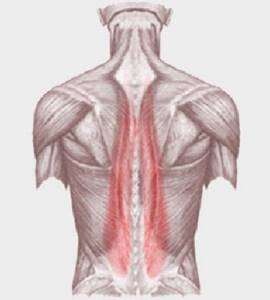
One of the most common types of gait disorders is the “sleeping” gluteal muscle. She should stabilize her pelvis when walking, but she doesn't. A whole cascade of muscle imbalances and characteristic pain arises. Pelvic instability is accompanied by weakness of the rectus abdominis, gluteus maximus and medius muscles, shortening of the piriformis, lumboiliac, quadratus lumbar, oblique and rectus femoris muscles. The function of the hip joint is disrupted, it begins to deteriorate and hurt, because the load is redistributed onto it.
The task of the gluteal muscle is to push the leg forward when stepping. Look at the photos of runners, they run with a straight body, without shifting the center of gravity forward, due to the strength of the gluteal muscles.
edella/depositphotos.com
If with each step the gluteal muscle pushes the leg forward, then not only the butt will become more beautiful, but also:
- the pelvis will be stable, it will not change its tilt, tilt to the sides or twist;
- the load will go away from the hip joints, they will stop collapsing and hurting;
- your step will become freer, and your gait will become easier and more beautiful.
And vice versa, if the gluteal muscle does not do its job, then:
- the iliopsoas and rectus femoris muscles gradually shorten, the step becomes heavy;
- the quadratus lumborum muscle becomes shortened or overstrained;
- the back extensors are overstrained, since the lumbar region is actively involved in the step;
- the pelvis becomes unstable;
- Pain occurs in the lower back, hip joints, and knees.
Diagnostics
Depending on the suspected etiology, duck gait is diagnosed by neurologists or orthopedic traumatologists. The collection of complaints and anamnesis involves establishing the time of onset and progression of gait disorders and the presence of other manifestations. The doctor assesses the dynamics of the development of the symptom, finds a connection with others with other diseases.
During a general examination, the specialist identifies external changes characteristic of myopathies (decreased muscle mass, protruded abdomen, winged shoulder blades), renal edema, bone deformities and other signs indicating the possible genesis of the disease. Based on the results of the survey and physical examination, the following are prescribed:
- Radiography
. For patients with congenital dislocation of the hip, photographs of the hip joints are taken; in case of sacroiliitis, an x-ray examination of the sacroiliac joint is performed; if urinary disease is suspected, x-rays of the deformed segments are performed. - CT scan
. Informative for orthopedic diseases, performed at the final stage of the examination, helps to clarify the severity and prevalence of disorders. - Magnetic resonance imaging.
Indicative in the diagnosis of congenital hip dislocations in young children. Allows you to reliably confirm the diagnosis when cartilaginous tissue predominates, which in patients of the younger age group is poorly visible on conventional radiographs. - Electrophysiological techniques
. ENG and EMG are the main methods used for the differential diagnosis of myopathies and other possible causes of muscle weakness (tumors of the central nervous system, myelitis, myelopathy). - Muscle biopsy.
Taking a biopsy sample and subsequent morphological examination of the material play a significant role in confirming myopathy and determining the form of the disease. The samples reveal an alternation of normal and atrophied myofibrils, inclusions of adipose and connective tissue. - Lab tests
. In patients with myopathy, an increased level of creatinine is found in the urine, and an increase in the concentration of LDH, AST, ALT, creatine phosphokinase and other enzymes in the blood. Genetic studies indicate relevant mutations.

Physiotherapy
Variants of incorrect gait
1. With each step, the pelvis tilts forward, causing a deflection in the lower back.

Photo by the author. Model - Serafima Konysheva, Iyengar yoga teacher
2. With each step, the pelvis twists to the right and left.
3. With each step, the weight is transferred to the hip joint, the pelvis tilts.

Photo by the author. Model - Serafima Konysheva, Iyengar yoga teacher
4. Shuffling gait, legs dragging along the ground with each step.

Photo by the author. Model - Serafima Konysheva, Iyengar yoga teacher
Myth number one: men look first at a woman’s legs.
Remember, when walking, men are attracted to women by the breasts, not the nose, forehead, head, chin, shoulders, hips or knees. Of course, when you take a step, your straightened leg will appear first, but the bottom of your leg is not at the man's eye level. Your breasts should be the center of attention; a man’s gaze should fall on them.
Try experimenting and see which part of your body is the most “outstanding” in the way you walk in life.
A beautiful gait requires slightly turned out toes: the starting position is heels together, toes apart, knees fully straightened and back straight. If you slouch when walking, it makes you look older and makes your breasts smaller, turning a size zero into a size minus one. The chest does not stand, but hangs on the belly. Some people walk leaning forward, and just in case they peck their nose - such a “birdlike” gait also does not add charm. Others walk on bent knees, trying to balance their heavy butts.
An exercise to help improve your gait
What should we do with the “sleeping” gluteal muscles? We need to start working with the shortened lumboiliac muscles and the muscles of the anterior thigh: make them functionally long. Stretch, in simple terms. This will align the pelvis and allow the gluteal muscle to engage in everyday activities.
It's better to start with a preparatory exercise. We will stretch the left iliopsoas and rectus femoris muscles.
Stand straight on two legs, take your right one back, the left one should remain vertical in line with the body. Place your right leg on the toe and straighten the knee, without moving the pelvis anywhere relative to the body. Already at this moment you can feel the tension on the front surface of the thigh, in front of the hip joint or slightly inside. Then we must stop at this position for now.

Photo by the author. Model - Serafima Konysheva, Iyengar yoga teacher
Please note that the pelvis should not follow the abducted leg. If this happens, it means that you are simply arching in the lower back and the exercise is useless. As you no longer feel the tension in your thigh, move your leg further and further.
In order for the gluteal muscle to participate in walking, the thigh must be stretched to approximately the length of a long stride. For running - a little more.
If you do this exercise for a week or two, you will notice that your step becomes freer, longer, and there is a desire to “turn on” your gluteal muscles.
BEAUTIFUL GAIT: WHAT DOES IT DEPEND ON, HOW TO PRESERVE IT?
A beautiful gait is the right gait. Correct from the point of view of human physiology (and not only), biomechanics.
GAIT is a set of individual characteristics, the manner of walking of an individual. It combines the motor skills of the free limbs with movements of the torso and head, including mechanisms for maintaining body posture and balance.
Figuratively speaking, gait is the “highlight” of our walking. And it is influenced by a huge number of factors, both objective and not so much. Many motor elements and signs that distinguish us from each other, and in some ways unite us, are determined by heredity, the presence of certain diseases, living conditions, etc. But no less formative factors are lifestyle, habits, profession and hobbies.
Changes in gait caused by objective factors
First of all, changes in gait cause problems (diseases, injuries) of the musculoskeletal system. Lameness is the most obvious example, but not the most common. Any pain syndromes of various origins affect gait immediately and can become fixed in muscle memory. A “vicious circle” may arise here:
PAIN SYNDROME - CHANGES IN THE BIOMECHANICS OF MOVEMENT - WEAKENING OF SOME MUSCLE GROUPS AND COMPENSATION AT THE EXPENSE OF OTHERS - PAIN SYNDROME - CHANGES IN THE BIOMECHANICS OF MOVEMENT (GAIT)…
Weakening of the body's muscular system due to age or a sedentary lifestyle also affects changes in gait. As a rule, these changes (within certain limits) are easily corrected. Physical exercise and systematic training will be an excellent prevention and therapy.
What gait is considered correct?
How many people we see around us whose gait is rather puzzling. It can be not just ugly (certain stereotypes still come into play here, but we’ll talk about them later), but defiant, repulsive, creating a certain image, a “portrait” that often distorts the true “face” of a person. Of course, “psychology” sometimes presents surprising behavioral patterns, but usually the most striking manifestations of INCORRECT gait have purely physiological reasons that cause a person, at a minimum, discomfort. They can be fairly easy to eliminate, although in some cases a doctor’s consultation and observation will be necessary.
How can you describe a correct gait?
- This is a “FROM THE HIP” movement. We have already said that gait is an individual feature of WALKING for a particular person (and not only), and walking (the most natural human locomotion, an automated motor act) is considered from the position of a “forward and reverse pendulum” - limb segments and the body - a system of physical pendulums. The frequency of oscillations (steps) depends on the length of the pendulum - the longer the length, the lower the frequency. By going “from the hip,” a person creates optimal conditions for the economical functioning of his system of pendulums. Much will depend on the desired speed of movement, but in any case, a long pendulum will require fewer oscillations (steps) to cover the required distance, thereby saving the body strength and time;
|
- A movement striving for “ONE LINE”. It is precisely the aspiring one who does not have to try to achieve the podium version. This is not accessible to everyone: often due to excessively developed adductor muscles or fat deposits on the inner thighs (something definitely needs to be done about the latter);
- FOOT POSITION STRAIGHT or almost straight. Exactly - without excessive inversion, unless, of course, this is a professional feature, as, for example, with ballet dancers. Why is this important for a beautiful (read – correct – physiological) gait? The same physics: the foot is a segment of the leg. You move forward, all segments of your body should move in the same direction, “do not dissipate” the general vector of movement;
- The knees are COMPLETELY EXTENSIVE, walking on half-bent legs (this is the sin of lovers of high heels) is not just ugly, but harmful;
|
- THE BACK IS STRAIGHT, the pelvis (lower back) is slightly forward, the physiological curves are slightly smoothed, the head looks straight (a few meters ahead, and not at the feet);
- THE SHOULDERS ARE LOWERED AND THE SHOULDS ARE REDUCED (without fanaticism);
- THE PRESS IS TONE (the stomach is tightened).
What muscles are “responsible” for a beautiful gait?
- RECTIVE MUSCLES OF THE BACK. “Without” them, without their proper development, it’s not so much that it’s beautiful to walk, but it’s simply not easy to live. These are DEEP muscles located to the left and right of the central axis (spinal column), their function is to straighten the body and form posture. With simultaneous (synchronous) contraction, the body straightens strictly along the midline - straight, when working on one side - the body will deviate in the corresponding direction.
|
- CORA muscles. There are many of them, they cover the torso, buttocks with a corset, and affect the back of the thigh. Their development and strengthening help to form beautiful posture and maintain a healthy spine. The abs (as a group of muscles that stabilize the core) are especially important when it comes to maintaining correct posture when moving;
|
- LEG MUSCLES, almost all large groups. Especially: 4-headed thigh muscles, calf muscles, foot muscles;
- You should also remember about the ligaments and fascia, which, together with the muscles, form the SOFT SKELETON of the body. The load on them is no less, and so is the pain and discomfort in case of injury or illness.
|
What should you do to form a beautiful gait?
- Exercises for the extensors of the back muscles: hyperextension, deadlift, lifting the torso from a prone position;
- Abdominal exercises: all possible types, including static and breathing;
- Exercise CALF RAISE, on both legs and alternately. A very important movement: the foot and calf muscles will work simultaneously, the quadriceps femoris muscle will be indirectly involved;
- Straighten your knees when walking (you need to take care of yourself, develop muscle memory);
- Watch your posture: straight, relaxed back, slightly tucked in stomach, head looking straight, shoulder blades pulled together, and shoulders down (not raised up or tense);
- When walking, feel the big toe and focus on it - include it in your work, this will make your gait elastic;
- Choose comfortable shoes and use preventive arch supports;
- Start the movement from the hip, trying to follow the “single line”. This requires some training and time. The main thing: complete relaxation of the movement (when moving your legs forward). What helps? Watching fashion shows from the best catwalks in the world, watching documentaries about animals (most predators and ungulates are excellent models), training at home to music in a free mode.
It will take you very little time to master the movement pattern; many people perceive it immediately, but strengthening and developing muscles will take more time if you are not used to loading yourself regularly. But even one-time exercises will bring success, at least you will know where and what muscles you “have”. If you exercise regularly, try adding more restorative procedures and relaxation procedures .
This article was prepared for you within the framework of the project of the Ministry of Sports and Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation - “Industry and Sports”. Learn from the champions!
Exercises for a beautiful gait
- Stand with your back to the wall so that your shoulders, shoulder blades, buttocks and heels touch the surface. Chest forward. Stand like this for a few minutes, remember the position of the body with your muscles. Stretch the top of your head 2-3 centimeters up. Try to maintain this posture when walking and sitting.
- Walk around the house with a book on your head. This way you will learn to maintain balance and practice a graceful gait. The main thing is don’t get too tight. You should carry the book casually, without thinking about it.
Never look at the camera when taking pictures!
If the photographer does not look at the camera, then the people around him do not even suspect that someone is photographing them. After all, do not forget that the main goal of shooting from the hip is to get images of people who behave naturally and at ease. Well, if while shooting you walk between people and always look at the camera hanging on your neck, then people, quite naturally, will pay attention to you and will act tense and constrained. If you do not look at your camera, do not raise it to your eyes, but look forward, to the sides, communicate with the people around you, or even avoid eye contact with the person you are filming, then you will become practically invisible to others . They will stop noticing you and paying attention to you. And then your pictures should turn out simply wonderful.
Use a wide angle!
If you try to shoot from the hip with a wide angle at least once, you will immediately feel how this lens itself involves you in the scene it is shooting. This is precisely where one of the main mistakes of those who are just starting to master this technique lies. The fact is that if you shoot from the hip with a 1.6x crop factor DSLR with a lens whose focal length is greater than 50 millimeters, then you will almost certainly achieve nothing. 50 millimeters is really too long a focal length for effective hip shooting.
But with an APS-C matrix much larger, any lens with a focal length of 17 millimeters (24-28 mm at full frame) is suitable for shooting from the hip. Using such a lens will give you a wider angle of view, and this will allow you to capture more space and more different objects within the frame.
Among other things, as we have already said, shooting from the hip with a wide angle allows the photographer to feel as if he is part of the action taking place in front of the lens.
Take as many photos as possible!
As we have already noted in this article today, photographing from the hip requires a lot of practice. If something doesn’t work out for you right away, of course, there’s no point in falling into despondency. So what if at first your pictures will be blurry, incorrectly constructed compositionally, or simply blurry. It was not us who said: repetition is the mother of learning. Photograph from the hip and, in general, photograph as much as possible! Experiment in different genres and shooting techniques! Fortunately, now, with the current digital photographic equipment, this is not at all expensive: after all, there is no need to buy photographic film and spend days in a darkroom, printing pictures on photographic paper. One old experienced photographer liked to say to his young colleagues: “He who takes a lot of photographs takes good photographs.” Another argued: “To learn photography, you need to take photographs.”
Take hundreds, thousands of pictures, spare no effort and time. “Rehearse” different techniques for shooting from the hip. Try, for example, a very low point - from the level of your feet, or even from the ground. Shoot from chest level. Try photographing people as if walking past them, with a camera that hangs vertically at your side. Or, from your hip level, take photos of unsuspecting people sitting on a bench in a park.
The possibilities of this technique - "shooting from the hip" - are truly endless. After some time, experience will come to you, and we think you will become a good master of street photography.