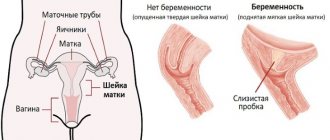
Sexual diseases in women are serious pathologies, extremely dangerous with serious consequences in the absence of timely treatment. They are provoked by various microorganisms: viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi. These are not only sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.), but also infections of the genitourinary organs (chlamydia, candidiasis, etc.).
A feature of sexual diseases is the absence of clearly defined symptoms, which is why they are often called hidden. A woman may not even suspect that she is infected for a long time. Symptoms are determined by factors such as the type of infection, the degree of damage to the genitourinary system and the body as a whole. Therefore, the manifestation of symptoms of sexual diseases is very diverse.
Syphilis
The content of the article
Typically, syphilis in women appears 2-4 weeks after infection, sometimes this period is reduced to 9 days or extended to 6 months. Clinical manifestations are divided into 3 stages: primary, secondary and tertiary.
The disease begins with the formation of a syphilitic ulcer - a flat, compacted papule - at the site of penetration of the pathogen:
- on the mucous membrane of the vagina, labia;
- on the nipples of the mammary glands;
- on the oral mucosa;
- in the corners of the lips;
- on the skin of the face.
The formation is painless, so many women do not even suspect its appearance when it is located inside the vagina and hidden from view. For this reason, syphilis is often diagnosed only in the secondary period. Over time, the papule turns from a small formation measuring 1-3 mm into a round or oval red ulcer with a diameter of up to 2 cm.
It has a dense structure and is moist to the touch. In the center the ulcer is dirty yellow in color, which resembles a purulent mass.
Symptoms of primary syphilis:
- enlarged lymph nodes near the sites of syphilitic ulcers (pelvic, submandibular or axillary). This occurs 5-7 days after the formation of hard chancre. They are painless, mobile, and can reach the size of a walnut;
- general malaise of the body: increased body temperature, fever, pain in bones and joints, weakness;
- copious thick discharge with a pus-like consistency and an unpleasant odor, sometimes causing itching and burning;
- menstrual irregularity, characterized by unpleasant sensations during bleeding.
Only 3-4 weeks after the formation of syphilitic ulcers, the RW blood test shows a positive result.
Treatment of breast diseases
Several basic approaches are used in the treatment of breast diseases.
Taking non-hormonal medications:
- potassium iodide to restore ovarian function (prescribed for mastopathy);
- vitamins;
- sedatives;
- diuretics for swelling of the mammary glands at the end of the menstrual cycle;
- hepatoprotectors, if the disease is associated with liver dysfunction;
- antibacterial drugs for severe inflammation (mastitis).
Hormone therapy:
- progestins;
- androgen drugs;
- drugs with antiprolactin activity;
- antiestrogenic drugs;
- oral contraceptives.
Local therapy:
- antiseptic compresses;
- ointments with anti-inflammatory action.
Surgical treatment:
- sectoral resection;
- in case of suppuration - evacuation of pus and installation of drainage;
- mastectomy - removal of the mammary gland. It can be performed for complications of inflammatory diseases, for breast cancer.
Breast cancer treatment methods:
- hormone therapy;
- radiation therapy;
- surgery;
- chemotherapy;
- combined and complex methods.
Important! Treatment tactics for breast cancer are tailored individually and depend on the stage at which the disease is detected, the subtype of cancer, medical history and other features.
Modern methods of treatment
Many methods traditionally used in the treatment of breast cancer are difficult to tolerate and are even considered mutilating, such as mastectomy (removal of the breast). Using modern methods, many serious consequences can be avoided without reducing the effectiveness of treatment.
Organ-preserving operations include:
- Lumpectomy - removal of only the tumor and a small amount of adjacent tissue. The method is used in the early stages in combination with radiation therapy and (not in all cases) chemotherapy.
- Oncoplastic operations. Carrying out lumpectomy with restoration of the original shape of the mammary gland immediately after tissue resection.
Breast reconstruction is an important part of treatment. When a woman goes to a doctor, she must be sure that the specialists will do everything possible to preserve the beauty of her body. Sometimes reconstruction can be done at the same time as a mastectomy. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy can be performed using the patient's own tissue or implants (the second option is preferable).
The importance of an integrated approach
When choosing a medical center where in-depth diagnostics and treatment will be carried out, you should pay attention to the range of services offered to patients. Thus, the Goldenes Kreuz clinic (Vienna, Austria) uses the latest methods for diagnosing and treating breast diseases. Early detection of a tumor becomes possible thanks to the introduction of such approaches as tomosynthesis and elastography in the medical center. The clinic’s specialists manage to preserve as much healthy breast tissue as possible, relying on their experience in performing breast-conserving operations (lumpectomy, oncoplastic surgery) and additional diagnostics (sentinel biopsy).
In addition, it is great if a woman can go through all the stages of fighting the disease in one center, trusting a close-knit team of doctors of different specialties. As a rule, the best results can only be achieved when treatment is approached on an individual basis. Such principles are followed, for example, in the Breast Health Center of the private clinic Goldenes Kreuz in Austria (video 1).
Video 1. Breast health center of the private clinic Goldenes Kreuz, Vienna, Austria.
Symptoms of secondary syphilis
The development of the secondary stage begins 2 months after the formation of compacted papules. The following symptoms may be observed:
- general malaise: headache, tinnitus, dizziness, poor appetite, high body temperature (up to 380C), pain in bones and joints, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, confusion. Speech disturbances and epileptic seizures may occur;
- dysfunction of internal organs (in 25% of cases): damage to the myocardium, liver, stomach, kidneys, membranes and blood vessels of the brain;
- loss of hair, eyelashes and eyebrows. Hair growth resumes after 1-2 months;
- the appearance of condylomas on the genitals and in the anal area;
- the occurrence of rashes on the skin, including the palms and soles of the feet, and mucous membranes.
The following types of rash are distinguished:
- syphilitic roseola - pink or pale pink flat spots from 0.5 to 1 cm in diameter. Localization – trunk and limbs;
- lenticular syphilide - copper-red round formations with a dense structure, rising above the skin;
- meliary syphilide - small dense formations with a diameter of up to 2-2.5 mm. They are brown in color and localized on the skin of the body. As a rule, such papules accumulate and form rings, arcs or plaques;
- coin-shaped syphilide - large red or brown formations with a diameter of up to 2.5 cm, slightly raised above the skin;
- weeping syphilide - eroded formations. They are moist, round in shape, and cause moderate itching. Localization – groin area and axillary folds;
- Condylomas lata are soft, pale pink formations that rise above the skin and are similar in appearance to papillomas. Localization – perineum and area around the mouth;
- pustular syphilide - small purulent formations with a yellowish crust at the end. Localization - on the skin of the trunk, limbs and face.
Usually after 3-5 weeks the rashes suddenly disappear, leaving no trace, even if no treatment was carried out. This period is called secondary latent syphilis. This stage lasts up to 5 years. During this time, relapses of the disease are observed, the rash appears again, but later also disappears on its own.
The course of the first wave of rashes is pronounced: multiple skin lesions, formations of a bright shade. Subsequently, darker elements are observed, often accumulating in groups.
Symptoms of tertiary syphilis
This type of disease is diagnosed extremely rarely. It develops 4-5 years after infection and is characterized by damage to the skin, mucous membranes, bones and internal organs. Over time it leads to death.
The symptoms are as follows:
- the appearance of brown or red-brown plaques on the skin. They have an uneven outline, rise above the skin, and are covered with ulcers and crusts. Localization – arms, back, face;
- formation in the subcutaneous tissue of an isolated gumma - a hard node the size of a walnut and an ulcer in the center. It usually occurs on the scalp, chest, face, and sometimes on the mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx and nose. In the latter case, tissue destruction and deformation of the palate occurs. Against this background, a number of complications develop:
- the nasal septum is destroyed and the nose is deformed;
- hoarseness and hoarseness appear;
- tongue mobility is impaired.
- damage to the nervous, vascular and skeletal systems, which manifests itself in the form of syphilitic meningitis, hydrocephalus, progressive paralysis;
- deformation and dysfunction of internal organs (liver, kidneys, lungs, heart).
The first signs of the disease
The first classic manifestation of gonorrhea is discharge. As a rule, they have a thick consistency, yellow or white color, an unpleasant odor, and cause itching. Against this background, women often mistake the disease for thrush or nonspecific colpitis, self-medicate and, thereby, erase the clinical picture.
Pain in the lower abdomen and when urinating may occur, and the urge to urinate may become more frequent. This is also often mistakenly blamed on cystitis or hypothermia.
Gonorrheal cervicitis
When the infection is localized in the vagina, the following symptoms are observed:
- yellowish-white discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- itching, burning and tickling sensation in the perineum and vagina;
- pain during intercourse.
In pregnant women, symptoms are more pronounced.
Inflammation of the appendages and uterus
When infection penetrates higher, the appendages and endometrium are affected. In this case it is observed:
- nagging or sharp cutting pain in the lower abdomen;
- purulent discharge mixed with blood;
- increase in body temperature to 38-390C;
- the appearance of signs of intoxication - weakness, malaise, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite;
- pain during intercourse.
Urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis
When the urethra is infected, the symptoms are as follows:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- cutting pain and burning during urination;
- swelling and redness of the external opening of the urethra, its palpation is painful, purulent discharge from it is possible;
- the appearance of a false urge to urinate.
- Ascending infection affects the bladder and kidneys.
Gonorrheal proctitis
Gonorrheal inflammation of the rectum causes:
- itching and burning in the anal area;
- mucopurulent discharge;
- painful bowel movements;
- false urge to defecate;
- bloody streaks in stool and discharge;
- purulent plaque on the rectal mucosa;
- redness of the anus;
- filling the folds of the anus with pus.
Gonorrheal pharyngitis
Usually hidden under the guise of an ordinary sore throat with characteristic symptoms:
- sore throat (rarely intense);
- pain when swallowing;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling and redness of the tonsils and palatine arches, the appearance of a yellowish-gray coating on them.
However, most often gonorrheal pharyngitis is asymptomatic or manifests itself only as a sore throat and hoarseness.
Gonorrheal stomatitis
It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- inflammation of the gums with the formation of purulent ulcers;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Gonorrheal conjunctivitis
Infection of the mucous membrane of the eyes causes vivid symptoms:
- swelling of the eyelids, which are literally glued together with purulent discharge;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- in advanced cases - clouding of the cornea and blurred vision.
Chronic gonorrhea
2 months after infection, gonorrhea takes on a chronic form, the clinical picture of which is almost erased. Asymptomatic periods of the disease are replaced by relapses with mild symptoms.
The trigger for an exacerbation can be hypothermia, the onset of menstruation, or termination of pregnancy. Symptoms include discharge and pain in the lumbar region, sometimes spasms can radiate to the legs or abdomen.
Chronic inflammation of the vaginal mucosa due to gonorrhea leads to menstrual irregularities. Bleeding is observed between menstruation, and the cycle itself becomes long and with heavy bleeding. As the disease progresses, adhesions develop in the pelvis.
A distinctive symptom of gonorrhea at this stage is the “morning drop” syndrome: when waking up, a woman may find a cloudy purulent drop at the opening of the urethra.
If left untreated, chronic gonorrhea can lead to infertility.
Trichomoniasis
The incubation period of the disease is 4-14 days, the first signs appear approximately 5 days after infection. Symptoms of trichomoniasis depend on the site of infection (vagina, urethra, and cervix).
Symptoms of “primary” trichomoniasis:
- copious discharge of leucorrhoea from the vagina. They are usually yellowish or greenish in color (may turn gray-green with blood streaks), foaming, and having an unpleasant odor. When combined with gardnerellosis (bacterial vaginosis), a “fishy” odor appears;
- the vaginal mucosa is covered with purulent discharge;
- vaginal discharge upon contact with the skin causes ulcers, irritations and abrasions to appear on it;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- burning and severe itching in the vagina, swelling and redness;
- intermenstrual bleeding from the vagina;
- when the urethra is affected by an infection, frequent urination, burning and cutting pain are observed;
- increase in body temperature to 37.50C;
- general deterioration of health, sleep disturbance;
- rarely – pain in the lower abdomen.
Signs and symptoms of gynecological diseases in women
To change the situation, all you need to do is visit your doctor regularly. In our clinic you will be consulted, examined as planned, and treated if there is anything for it.
Causes
Before you start talking about the symptoms and signs of gynecological diseases, you should still understand the reasons for their occurrence. Conventionally, they are divided into external and internal factors.
External factors:
- severe stress of a constant or periodic nature;
- deterioration of the environmental situation;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- onset of sexual activity at an early age;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- infectious diseases;
- injuries;
- taking antibiotics frequently and uncontrollably.
Internal factors:
- improper development of the reproductive system;
- disturbances in the location of the genital organs;
- hormonal imbalances;
- tumor processes.
Symptoms and signs of diseases
There are an almost limitless number of them, but from this infinity, 5 main ones can be distinguished. If you observe at least one in yourself, then this is already a reason for concern and see a doctor. So:
1. Vaginal discharge
All women experience them from time to time, and in some cases they are even considered the norm. They turn into a symptom of the disease if they are permanent, released in large volumes and have an unpleasant odor, accompanied by pain and itching. With pathologies, the discharge is most often thick and has a different color than normal. Based on the nature of the discharge, you can independently determine the causative agent of the disease:
- with a bacterial infection, the discharge will have a greenish tint with a fishy odor;
- with a fungal disease, the discharge is thick and cheesy;
- In case of cancer, the discharge is watery mixed with blood.
At your appointment, our specialists will definitely ask you when the discharge begins (in what period of the cycle), what is its nature (periodic, constant), and whether there are additional symptoms (pain, itching, burning). Therefore, watch your body.
For your peace of mind, we note that discharge may appear for other more harmless reasons:
- The personal hygiene products or washing powder you use to wash your underwear are not suitable;
- presence of a foreign body in the vagina;
- allergy to condoms or other means of mechanical contraception;
- incorrect underwear (synthetic and tight);
- excessive hygiene.
2. Painful sensations
Depending on the disease, pain can be of different types and intensity:
- inflammatory diseases are indicated by aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- if the pain is acute and paroxysmal, then this may indicate a rupture of the ovary or fallopian tube, torsion of an ovarian cyst or ectopic pregnancy;
- during abortion, the pain will be cramping;
- If you wake up with aching pain at night, this may indicate cervical cancer or genital endometriosis.
It is worth paying tribute to the psychological factor. We often encounter imaginary pain when it is provoked by the patient herself due to excessive worry.
3. Bleeding , which is divided into genital and extragenital.
The causes of genital bleeding are:
- menstrual dysfunction;
- inflammatory diseases;
- neoplasms (fibroids);
- genital injury.
Causes of extragenital bleeding:
- severe hypertension (more common in menopausal women);
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- severe infectious diseases (for example, hepatitis).
4. Itching of the vulva
Most often, this symptom occurs in women in menopause, and this symptom occurs with gynecological diseases caused by infections, diabetes or intoxication.
5. Disruption of the work of related organs
The rectum suffers first, and constipation can occur against the background of large tumors, cicatricial adhesions or purulent processes. The bladder may also be affected by a tumor.
6. Disorders associated with the menstrual cycle
On this list are the familiar PMS (premenstrual syndrome) and the unpleasant dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation).
PMS is well known to both women and men who communicate with them, and everyone suffers from it. It begins one to two weeks before the onset of monthly bleeding and consists of nervousness, irritability, depression, emotional outbursts, headaches, swelling, and tenderness of the mammary glands. And all because of the hormones at play. If the symptoms do not interfere with your life, then this is good, otherwise you need to consult a doctor.
Dysmenorrhea is the appearance of painful sensations during menstrual bleeding. The pain can be so severe that it radiates to the lower back and legs. At the same time, it is dull or spasmodic in nature. Typically, such severe pain is not normal, so if you experience it, consult a doctor immediately.
Diagnosis and treatment
When you contact our clinic, a specialist will first examine you, then conduct a conversation - approximately according to the plan presented above. Then you will need to undergo some tests so that the doctor can make a correct and accurate diagnosis.
After this, strictly individual treatment is prescribed. Inflammatory diseases are never treated with general methods, and there is no specific algorithm for this. Only an individual approach and strict control of patients who contact us allows us to help them quickly and effectively.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an insidious disease, since in 6% of cases it is asymptomatic, which does not mean safety. The incubation period is 2-4 weeks, after which symptoms may appear:
- itching and burning on the genital mucosa;
- white or yellowish mucopurulent discharge with a sharp, unpleasant odor;
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.50C;
- minor or intense pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar and groin areas, intensifying before menstruation, with sudden movements and physical activity;
- when the mucous membrane of the urethral canal is infected: frequent urination, pain, itching and burning during urination, cloudy urine;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- slight bleeding during or after sexual intercourse;
- erosion of the cervix, small ulcerations on it and spotting;
- in advanced cases - a violation of the endocrine function of the ovaries and the ovarian-menstrual cycle, as a result of which menstruation becomes irregular, painful, rare, abundant or, conversely, scanty.
Often, with a long asymptomatic course, the only sign of the disease is infertility.
Causes of gynecological diseases
The causes of gynecological diseases are conventionally classified into external and internal.
External factors include:
- constant or periodic, but strong stress reactions of the body to external stimuli;
- the deteriorating environmental situation observed in cities;
- frequent changes of sexual partners;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules and, as a result, the development of frequent infectious diseases;
- infectious diseases as a risk of developing symptoms of gynecological diseases;
- frequent and uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
Among the internal factors are:
- abnormalities in the development of the female genital organs, for example, the presence of a bicornuate uterus or vaginal duplication;
- incorrect location of the internal genital organs;
- hormonal diseases;
- abortions or spontaneous miscarriages, as a result of which medical interventions were performed, in particular uterine curettage.
Actinomycosis
This disease is quite rare. At the initial stage, the symptoms of actinomycosis are mild and often resemble an inflammatory process.
Observed:
- increase in body temperature up to 400C;
- sharp or aching pain in the lower abdomen and iliac region.
As the disease progresses, dense, painless infiltrates form. All pelvic organs are involved in this process, deformation changes occur in the uterus, appendages, intestines, rectum with hyperemia of the mucous membrane and smoothness of the vascular pattern. Large dense infiltrates can compress the intestines and disrupt the functions of the urinary tract.
At the next stage of the disease the following is observed:
- the formation of fistulas with purulent discharge, spreading to the retroperitoneal tissue, bladder, thigh and rectum. In this case, the secreted pus has no odor;
- disturbances of menstrual (acyclic bleeding, absence of menstruation) and reproductive function.
In the chronic form of the disease, adhesions and scars appear.
Mycoplasmosis
In 10-20% of cases, this disease is asymptomatic until it is activated by various stress factors: abortion, hypothermia, nervous strain, etc. The incubation period ranges from 5 days to 2 months, with the first signs appearing approximately 7-14 days after infection.
Mycoplasmosis does not have clearly defined specific symptoms; they depend on the clinical form of the disease. The pathology can occur in the form of vulvovaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, adnexitis, urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
The following clinical picture is observed:
- if the vagina and cervix are affected: yellow or gray mucous discharge, itching and burning during urination, discomfort and pain during or after sexual intercourse;
- with damage to the uterus and appendages: nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, intermenstrual bleeding, menstrual irregularities;
- when the urethra is infected: frequent urination, pain and burning during it, false urge to urinate, increased body temperature up to 38.50C, cutting pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the lower back;
- with intestinal damage: pain during defecation, false urge to defecate, sometimes - an admixture of mucus in the stool;
- if the respiratory system is affected (does not apply to sexual diseases, but can become a complication of genital mycoplasmosis): sore throat, nasal congestion, inflammation of the ligaments, bronchitis, fever, weakness, sweating, long-lasting cough with sputum.
Gynecological diseases: symptoms and causes
Gynecological diseases are diseases of the female genital organs that can manifest themselves with various symptoms and signs. The most common reasons for their occurrence include:
- Injuries
- Infections
- Hormonal imbalances
Today, gynecological diseases among women are quite common, which is due to factors not only from the environment, but also from the internal environment of the body itself.
Gynecological diseases and their types

Conventionally, all gynecological diseases can be divided into three groups depending on the cause of their occurrence and the specificity of their manifestation. These include:
- Infectious.
The cause of their occurrence is various infections that enter the body. - Hormonal.
Diseases in this group are caused by endocrine pathologies, as well as hormonal imbalances. - Tumor.
Such diseases most often arise as a result of injuries and manifest themselves in the form of tumor processes, as well as hypertrophic and dystrophic changes.
It is worth noting that gynecological diseases are increasingly common in women of both young and older ages. However, they may not have symptomatic manifestations, which makes their self-diagnosis extremely difficult.
The main causes of gynecological diseases include:
- External:
environmental deterioration, poor hygiene, indiscriminate change of sexual partners, spontaneous use of antibiotics, frequent stress reactions arising from external stimuli, etc.
- Internal:
abnormalities in the development of the genital organs, abortions, hormonal pathologies, incorrect location of internal organs, etc.
Only a qualified medical professional can determine the cause of the disease and eliminate it.
Symptoms of gynecological diseases
There are a huge number of different external and internal manifestations that can be used to determine the presence of gynecological diseases in women. The most common of them include:
- Itching or burning in the genital area.
- Discharge from the genitals.
- Pain in the lower abdomen during the non-menstrual period.
- Unpleasant or painful sensations during urination, etc.
In order to definitively confirm the presence of a particular gynecological disease, professional diagnosis by a qualified specialist is necessary. For the fastest and most effective solution to problems, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist. This will allow you to prevent the development of certain diseases in advance, as well as begin treatment of existing ones in a timely manner.

Our medical center is ready to provide an extensive list of services for the diagnosis and treatment of gynecological diseases of various types. We employ qualified doctors who are able to quickly diagnose the disease and correctly adjust the course of treatment to achieve the fastest and most effective results.
In addition, they have modern equipment and medications at their disposal, which also has a positive effect on the effectiveness of treatment. Gynecological diseases in Orenburg, and in particular, their treatment and diagnosis will no longer be a problem for you. Come to ours and we will provide you with professional medical care.
Ureaplasmosis
In 70-80% of cases, there are no clinical manifestations of this disease, therefore, as a rule, it is detected during the diagnosis of another disease. Ureaplasmosis has no specific symptoms and during periods of exacerbation it manifests itself as an inflammatory process. The incubation period can last from several days to several months.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- urethritis (inflammation of the urethra): pain and burning in the urethral area, while the pain increases sharply when urinating, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the external urethral os, frequent urination;
- mucous discharge from the vagina and urethra. They are usually quite scanty, odorless and colorless. If the inflammatory process has already started, the discharge may become greenish or yellowish and take on a sharp, unpleasant odor;
- painful and uncomfortable sensations during and after sexual intercourse;
- bloody discharge from the vagina after sexual intercourse;
- aching or nagging pain in the lower abdomen. If the disease has caused complications in the appendages and uterus - pain in the lower abdomen of a cutting nature;
- in acute form: increase in body temperature to 37-37.50C; weakness, fatigue, decreased performance;
- in the chronic form: infertility, spontaneous miscarriage, pathological course of pregnancy, treatment-resistant urethritis, vaginitis, endocervicitis, adnexitis.
If the infection occurs during oral sex, ureaplasmosis can be hidden under the “mask” of a sore throat: plaque appears on the tonsils (tonsils), painful sensations in the throat, it is difficult and painful to swallow, etc.
III. Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs of specific etiology.
Trichomoniasis is an infectious disease caused by Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomoniasis is transmitted sexually. Most often, Trichomonas affects the vagina, less often - the urethra, bladder, excretory ducts of the large glands of the vestibule of the vagina, the vestibule itself, the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, and appendages. Trichomoniasis is characterized by multifocal lesions.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by gonococci. The main route of infection with gonorrhea is sexual. Gonorrhea is characterized by predominant damage to the mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs. There are two ways of spreading gonorrhea: ascending - urethra, cervix, endometrium, tubes, peritoneum and hematogenous - penetration of gonococci into the bloodstream. Topographically, ascending gonorrhea, urinary gonorrhea, rectal gonorrhea, and metastatic gonorrhea are distinguished. According to the clinical course, fresh and chronic gonorrhea are distinguished. Fresh gonorrhea, in turn, is divided into acute, subacute and torpid. There are the following inflammatory processes of gonorrheal etiology: gonorrheal urethritis, gonorrheal bartholinitis, endocervicitis, gonorrheal proctitis, gonorrheal endometritis, salpingoophoritis, oophoritis, gonorrheal pelvioperitonitis, ascending gonorrhea. Gonorrheal infection is observed in 5-25% of patients, ranking second after trichomoniasis.
Candidiasis is a disease caused by yeast-like fungi. Fungi of the genus Candida are part of the normal microflora of a healthy person, but under certain conditions they can cause a disease - candidiasis. There are candidiasis of the vulva, vagina, uterus and uterine appendages.
Viral diseases of the genital organs are caused by two groups of viruses. Damage to the uterus, fallopian tubes and bladder is caused by the herpes virus, while damage to the cervix and urethra is caused by a urogenital virus. The causative agent of genital warts is a filterable virus.
Mycoplasmosis (ureaplasmosis ) is a disease caused by a group of microorganisms of the mycoplasma and ureaplasma family, which are part of the normal microflora, but under certain conditions exhibit pathogenic properties.
Chlamydia is a disease caused by chlamydia. Chlamydia etiology can include colpitis, cervicitis, erosion, urethritis, salpingitis, proctitis, etc.
Tuberculosis of the female genital organs. Tuberculosis is a common infectious disease, one of the local manifestations of which is damage to the genital organs. Tuberculosis of the genital organs is a secondary process, the primary source of which is the tuberculosis focus. According to the localization of the process, tuberculosis of the appendages, uterus, cervix, vagina, and vulva is distinguished. The course can be acute, subacute and chronic. Tuberculosis of the genital organs can occur in combination with pulmonary tuberculosis (up to 90%).
Gardnerellosis
The incubation period of the disease is 4-10 days. The first signs of infection are:
- the appearance of a “rotten fish” smell from the vagina. This specific odor is caused by the breakdown of waste products of the infection;
- slight whitish-gray or yellowish vaginal discharge.
- With the development of the disease, the clinical picture is supplemented by symptoms:
- feeling of irritation, itching and burning in the vagina;
- frequent urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which indicates an increase in the inflammatory process;
- increasing discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- creamy discharge flowing down the walls of the vagina into the perineum.
After sexual intercourse, the symptoms become more pronounced, since sperm, having an alkaline reaction, serves as a favorable environment for the proliferation of gardnerella bacteria.
Candidiasis (thrush)
The first signs of candidiasis (thrush) appear already 4-5 days after infection or activation of the vagina’s own opportunistic microflora. The clinical picture of this disease is as follows:
- pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse: the vaginal mucosa is destroyed by Candida fungi, becoming inflamed and painful;
- burning and itching in the genital area. These symptoms are worse after urinating or washing;
- swelling and redness of the genitals;
- white coating and copious “curdled” discharge with an unpleasant sour odor. The discharge is mucus with many white dense lumps (a type of curdled mass or curdled milk);
- pain and discomfort when urinating;
- the appearance of a rash on the labia. With thrush, the formation of small burgundy pimples-vesicles with liquid contents inside - vesicles - is often observed. After 1-2 days they burst and small erosions and crusts form in their place;
- general deterioration of condition. The listed symptoms cause nervousness, attacks of bad mood, and sleep disturbances (the burning sensation intensifies at night). Their manifestation is especially intensified after a long walk and during menstruation.
I. Inflammatory processes in the lower genital organs.
Vulvitis is an inflammation of the external female genitalia. Primary vulvitis occurs as a result of injury followed by infection (itching, scratching, abrasions, etc.). Secondary vulvitis in women occurs when there is an inflammatory process in the internal genital organs.
Bartholinitis is an inflammation of the large gland of the vaginal vestibule.
Colpitis is an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. The inflammatory reaction can be either focal or diffuse, spreading to the vaginal part of the cervix and vulva.
Endocervicitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. The occurrence of endocervicitis is facilitated by ruptures of the cervix (during childbirth, abortion), diseases of other parts of the reproductive system.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
The forms of manifestation of the papilloma virus in women are different: genital warts, flat warts, dysplasia, bowenoid papulosis, precancerous condition and cervical cancer. Usually, papillomavirus occurs latently and is detected during a routine examination. Pathological changes in the skin are usually detected 1–6 months after infection.
The incubation period and the main manifestations of symptoms depend on the type of papillomavirus, its quantity (viral load), immune activity and concomitant diseases (sexually transmitted infections).
The following are the main symptoms of HPV in women:
| Symptom | Condylomas acuminata | Dysplasia | Cervical cancer |
| Pain in the lower back, lower limbs and pelvis | No | No | Eat |
| Intermenstrual bleeding | No | Eat | Eat |
| Minor bleeding after intercourse | Eat | Eat | Eat |
| Discharge | Transparent or yellowish-green color with an unpleasant odor | With an unpleasant odor | With an unpleasant odor |
| Itching and burning in the genital area | Eat | Eat | Eat |
| Pain during and after intercourse | Eat | Eat | Eat |
The clinical picture can be supplemented by general signs:
- chronic fatigue;
- periodic weight loss;
- decreased appetite;
- swelling of the lower extremities.
Diagnostics
Pain, burning, itching in the vagina, discharge with an unpleasant odor are good reasons to consult a doctor.
In order to identify female diseases and clarify the diagnosis, the following research methods are used:
- laboratory (smear taking, etc.);
- ultrasonic;
- minimally invasive (endoscopic and laparoscopic).
A comprehensive examination will allow not only to make a correct diagnosis, but also to recognize the disease at a very early stage and, thus, prescribe the necessary treatment in a timely manner.
If we are talking about an infection, it is important to treat the sexual partner as well. Otherwise, re-infection may occur.
Herpes infection (cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex)
Primary herpes
Primary herpes occurs in 5 periods:
- Incubation . Lasts from 2 to 14 days, there are no symptoms;
- Prodromal . General and local manifestations increase: malaise, muscle pain, accompanied by swelling and weakness, increased body temperature to 37-37.50C, possible chills, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes. There is also itching and burning in the genital area, leucorrhoea, painful urination with pain and burning;
- Rash period . The duration of the period is from 7 to 10 days. The appearance on the vaginal mucosa of rashes in the form of bubbles with a diameter of 2-3 mm with liquid contents - vesicles. They accumulate in groups, forming a painful, itchy area. Periodically, the number of rashes increases. General symptoms are mild, local manifestations in the form of itching, burning, swelling and pain persist. They lead to nervousness, attacks of bad mood, sleep disturbances;
- Stabilization period . Lasts about 2-3 weeks. At this stage, the vesicles become cloudy, open and form weeping erosions that are prone to fusion. Sometimes ulcers up to 1 mm deep appear in their place. The affected areas are painful, purulent plaque is possible, there is no bleeding;
- Healing period . Lasts about 2-3 weeks. Local and general symptoms subside. The affected areas dry out, a thin crust forms, under which a new epithelium forms. After a while, the crust disappears, and in its place there is redness, which goes away after complete healing.
The rash is usually localized near the external opening of the urethra, at the vaginal opening, on the labia, on the cervix, in the anus or buttocks.
The total duration of primary herpes is 5-7 weeks.
Recurrent herpes
Recurrent herpes can occur in typical and atypical forms. The typical form is characterized by the same symptoms as primary herpes. Only the total duration is 7-10 days.
The atypical form can be presented in various ways:
| Option | Predominant symptoms |
| Hydropic | Diffuse swelling and redness of the vulva |
| Itchy | The appearance of deep, poorly healing cracks, severe itching of the vaginal mucosa |
| Abortive | Absence of some stages of the disease, regression of rashes in 2-3 days |
| Subclinical | Presence of microsymptoms (itching, superficial cracks) or absence of clinical manifestations |
Lymphogranuloma venereum
The incubation period of the disease ranges from several days to 4 months. The development of the pathological process occurs in 3 stages.
Symptoms at stage 1:
- the appearance of bubbles at the site of infection;
- after a few days, the rash turns into purulent round ulcers with a diameter of 1-3 cm;
- pathological vaginal discharge;
- enlarged pelvic lymph nodes.
Foci of infection can appear not only on the vaginal mucosa, but also on the wall of the rectum (if infected through anal sex), and in the oral cavity (if infected through oral sex). After 2 places after infection, the signs of inflammation intensify: stage 2 of the disease begins.
The following symptoms are observed:
- enlargement of the pelvic lymph nodes with greater intensity and inflammation of the surrounding tissues, their soreness;
- the occurrence of fistulas inside an extensive tumor with purulent discharge;
- the development of adhesions, which causes a violation of the outflow of lymph, and the genitals swell;
- pain when urinating and during sexual intercourse;
- general weakness, lethargy, drowsiness;
- rapid loss of body weight;
- loss of appetite;
- pain and aches in joints and muscles (evidence of the spread of infection throughout the body);
- sometimes - the appearance of eczema, urticaria and other lesions on the skin.
When the rectum is infected, the pain spreads to the lower back, and a small lump is felt near the anus. There is a disturbance in the process of defecation: frequent constipation, pain and burning during bowel movements.
In the absence of adequate therapy, after 1.5-2 years the disease enters stage 3, characterized by a number of complications. It is characterized by the following clinical picture:
- the occurrence of genitoanorectal syndrome (inflammation of the perineum, perianal region, rectum and surrounding tissue) at the site of inflammatory and adhesive phenomena;
- nagging pain and purulent discharge from the anus;
- erosion, pain and bleeding in the lower rectum;
- the appearance of ulcers, fistulas and abscesses in the anorectal region and perineum;
- deformation of the labia up to elephantiasis, narrowing of the vaginal opening.
With the development of necrotic phenomena in the inflamed lymph nodes, a general deterioration of the condition (chills, fever, cold sweat, nausea, vomiting, fever) may be observed at the 2nd stage and continue into the 3rd stage. The lymphatic system, which has been attacked by an infection, spreads it throughout the body, causing damage to the spleen, liver, venous inflammation, eye diseases, and the development of arthritis.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter